Mybatis源码分析之(三)mapper接口底层原理(为什么不用写方法体就能访问到数据库)
mybatis是怎么拿sqlSession
在 上一篇的时候,我们的SqlSessionFactoryBuilder已经从xml文件中解析出了Configuration并且返回了sessionFactory。
然后我们要从session;中拿到sqlSession
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {private final Configuration configuration;@Overridepublic SqlSession openSession() {//默认情况下ExecutorType是ExecutorType.SIMPLE类型的return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);}private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {Transaction tx = null;try {//获取配置的环境信息final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();//获取environment中的TransactionFactoryfinal TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);//生成Transactiontx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);//生成Executor(重要,之后的查询都得靠它)final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);//返回DefaultSqlSessionreturn new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);} catch (Exception e) {closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);} finally {ErrorContext.instance().reset();}}}//DefaultSqlSession类的组成,其实新建的时候就只是把他的字段赋值而已public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {private Configuration configuration;private Executor executor;private boolean autoCommit;private boolean dirty;private List<Cursor<?>> cursorList;}public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor, boolean autoCommit) {this.configuration = configuration;this.executor = executor;this.dirty = false;this.autoCommit = autoCommit;}
上面分析的是到拿到sqlSession为止,重点其实不是在上面这里,因为到上面为止,其实主要的功能只是将配置的信息解析成我们要的类,然后进行初始化赋值。
Mapper的实现原理
下面我们从SqlSession中拿到mapper,并执行方法其实才是,你感觉到mybatis框架开始帮我们做事的开始。
public static void main(String[] args) {//拿到SqlSessionSqlSession sqlsession = MybatisUtil.getSqlsession();//拿mapperTDemoMapper mapper = sqlsession.getMapper(TDemoMapper.class);//调用mapper的方法List<TDemo> all = mapper.getAll();for (TDemo item : all)System.out.println(item);}
因为我们在项目中的TDemoMapper只是一个接口,并没有实现这个接口方法,但是为什么我们在调用这个接口方法的时候就可以得到返回结果呢?mybatis究竟做了什么?
首先我们回到之前解析Mapper的语句
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {if (parent != null) {for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);} else {String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) { //根据resource解析ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());mapperParser.parse();} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {//根据url 解析ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());mapperParser.parse();} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {//根据mapperClass解析//首先通过mapperClass的路径,生成mapperClass的接口类Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);//降mapperClass加入到configuration中去configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);} else {throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");}}}}}//Configuration类下public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {mapperRegistry.addMapper(type);}//MapperRegistry类下public class MapperRegistry {private final Configuration config;private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>>();//最终调用这个方法public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {if (type.isInterface()) {if (hasMapper(type)) {throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");}boolean loadCompleted = false;try {//将接口包装成MapperProxyFactory类放入knownMappers中(knownMappers就是存放我们的mapper接口的)knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.//通过这个builder来解析mapper的statement。(把mapper和mapper.xml文件相关联,方法名与xml中的id相关联,为了之后调用的时候能找到的语句)MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);//开始解析parser.parse();loadCompleted = true;} finally {if (!loadCompleted) {knownMappers.remove(type);}}}}}//MapperAnnotationBuilder类中public void parse() {String resource = type.toString();if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {//通过xml文件解析loadXmlResource();configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());parseCache();parseCacheRef();//获得接口的方法(为了获取方法上的注解,通过注解的方式来让方法于sql语句相关联)Method[] methods = type.getMethods();for (Method method : methods) {try {// issue #237if (!method.isBridge()) {//具体的解析过程parseStatement(method);}} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));}}}parsePendingMethods();}
具体的调用过程就不细跟了,无非就是获取节点,获取属性值,(或者是获取方法,然后获取注解信息),巴拉巴拉……然后设置到configuration中。
上面要注意的点是,若既配置xml又配置注解的情况下,注解会覆盖xml,原因非常简单,源码中注解解析在xml解析后面,然后覆盖的情况是,他们有相同的namespace+id。
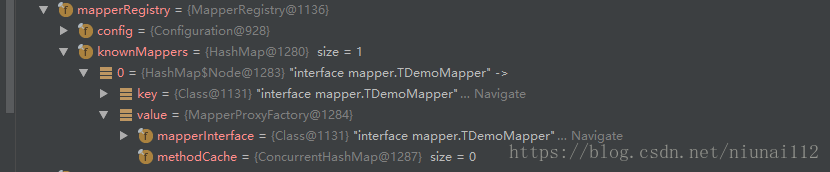
然后我们继续我们的主线任务,就是mapper的设计架构。从上面我们可以知道,configuration中有一个MapperRegistry类型的字段mapperRegistry,其中有一个字段叫knownMappers,knownMappers里面存着key为接口类型,值为MapperProxyFactory的。
//我们在调用TDemoMapper mapper = sqlsession.getMapper(TDemoMapper.class);的时候//先调用DefaultSqlSession类下的@Overridepublic <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);}//然后调用Configuration类下的public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);}//最后调用MapperRegistry类下的public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");}try {//实际生成是这段代码,通过mapperProxyFactory来生成实例对象return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);} catch (Exception e) {throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);}}//实际调用类public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {private final Class<T> mapperInterface;private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>();public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {//实例化一个代理类final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);//通过这个函数实例化return newInstance(mapperProxy);}protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {//动态代理的基本操作(说明最终实现方式是动态代理)return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);}}public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;private final SqlSession sqlSession;private final Class<T> mapperInterface;private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {this.sqlSession = sqlSession;this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;this.methodCache = methodCache;}//动态代理中最重要的方法invoke@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {try {if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {//如果是Object中的方法就不走下面的代理了,直接执行(比如toString,hashCode)return method.invoke(this, args);} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {//如果不是静态方法而且不是抽象方法,则不增强方法return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);}} catch (Throwable t) {throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);}//实际我们的mapper接口的方法走的逻辑就是下面这2条final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);}}
总结
我们通过sqlSession获得mapper方法,而sqlSession从configuration中的mapperRegistry中获取MapperProxyFactory对象,在通过MapperProxyFactory对象的newInstance方法得到MapperProxy的动态代理实例对象。
我们使用的mapper其实是通过MapperProxy动态代理,在运行时候生成的一个新的对象进行方法增强的,里面的接口方法都会通过下面2个语句进行数据库的操作,以及后续对数据的处理
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);12
这两条语句其实包含对访问数据库对象的创建,访问数据库到得到数据库返回数据后的处理等内容,非常复杂,本篇就到此为止。
版权说明 : 本文为转载文章, 版权归原作者所有 版权申明
原文链接 : https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43842093/article/details/122422061
内容来源于网络,如有侵权,请联系作者删除!