POI 富文本RichTextString
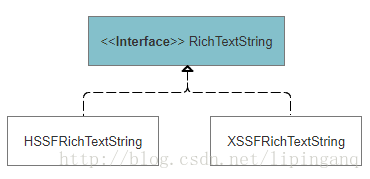
1. 富文本RichTextString概述
富文本unicode字符串可以将字体Font应用于字符串的任何部分:
applyFont(int startIndex, int endIndex, Font font)
applyFont(int startIndex, int endIndex, short fontIndex)2. HSSFRichTextString
创建HSSFRichTextString单元格的方式很重要,有时,创 建太多的HSSFRichTextString单元格会导致Excel 2003和 更低版本在更改单元格的颜色,然后保存Excel文件时崩溃
第一种:
HSSFCell hssfCell = row.createCell(idx);
RichTextString str = new HSSFRichTextString("富文本");
str.applyFont(0, 1, font1);
str.applyFont(1, 3, font2);
hssfCell.setCellValue(str);第二种:
// 创建单元格样式style, 并为其分配第一个字体font1
CellStyle style = workbook.createCellStyle();
style.setFont(font1);
Cell cell = row.createCell(idx);
cell.setCellStyle(style);
RichTextString str = new HSSFRichTextString("富文本");
// font2将覆盖font1
str.applyFont(6, 13, font2);
cell.setCellValue(str);要将不同的字体Font应用于富文本字符串的不同部分一般采用第二种方法
package hssf.sheet.richtextstring;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFRichTextString;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.CellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Font;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
public class ExportHSSFRichTextString {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\test.xls");
if (file.exists()) {
file.delete();
}
BufferedOutputStream out = null;
try {
out = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\test.xls"));
exportExcel(out);
} finally {
out.close();
}
}
private static void exportExcel(BufferedOutputStream out) throws IOException {
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("富文本");
sheet.setColumnWidth(2, 150*256);
Row row = sheet.createRow(5);
Cell cell = row.createCell(2);
CellStyle style = workbook.createCellStyle();
cell.setCellStyle(style);
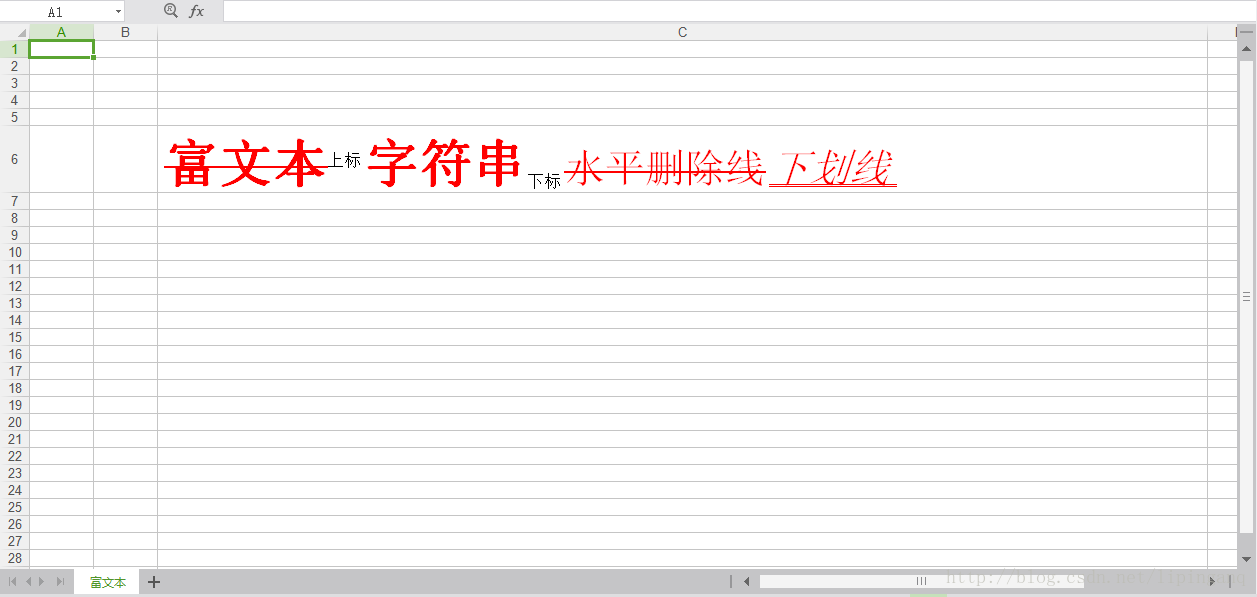
HSSFRichTextString str = new HSSFRichTextString("富文本上标 字符串下标 水平删除线 下划线");
/**********************************第一个字体Font:富文本0-3******************************************************/
// 在workbook中创建一个字体
Font font1 = workbook.createFont();
// 设置字体为粗体
font1.setBold(true);
// 设置字体的字符集 - 默认字体集
font1.setCharSet(Font.DEFAULT_CHARSET);
// 设置字体的高度 - 以1pt的1/20位单位
font1.setFontHeightInPoints((short)40);
// 设置字体的名字
font1.setFontName("宋体");
// 设置文字为斜体
font1.setItalic(false);
// 使用水平删除线
font1.setStrikeout(true);
// 设置字体颜色为默认黑色
font1.setColor(Font.COLOR_RED);
style.setFont(font1);
/**********************************第二个字体Font: 上标3-5******************************************************/
Font font2 = workbook.createFont();
// 设置上标字体高度为30pt
font2.setFontHeightInPoints((short)20);
// 设置为上标
font2.setTypeOffset(Font.SS_SUPER);
str.applyFont(3, 5, font2);
/**********************************第三个字体Font: 字符串6-9******************************************************/
Font font3 = workbook.createFont();
// 设置字体高度 - 以1pt为单位, 设置字体为60pt
font3.setFontHeightInPoints((short)40);
font3.setBold(true);
// 设置字体的字符集 - ANSI字符集
font3.setCharSet(Font.ANSI_CHARSET);
// 设置字体颜色为深红色
font3.setColor(Font.COLOR_RED);
str.applyFont(6, 9, font3);
/**********************************第四个字体Font: 下标9-11******************************************************/
Font font4 = workbook.createFont();
// 设置为下标
font4.setTypeOffset(Font.SS_SUB);
// 设置下 标字体高度为30pt
font4.setFontHeightInPoints((short)20);
str.applyFont(9, 11, font4);
/**********************************第五个字体Font: 水平删除线12-17******************************************************/
Font font5 = workbook.createFont();
// 设置下 标字体高度为30pt
font5.setFontHeightInPoints((short)30);
font5.setColor(Font.COLOR_RED);
font5.setStrikeout(true);
str.applyFont(12, 17, font5);
/**********************************第六个字体Font: 下划线18-21******************************************************/
Font font6 = workbook.createFont();
// 设置下 标字体高度为30pt
font6.setFontHeightInPoints((short)30);
font6.setColor(Font.COLOR_RED);
font6.setItalic(true);
// 设置字体双下划线
font6.setUnderline(Font.U_DOUBLE);
str.applyFont(18, 21, font6);
cell.setCellValue(str);
workbook.write(out);
}
}3.XSSFRichTextString
3.1 共享字符串
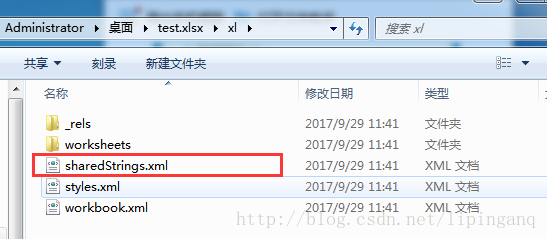
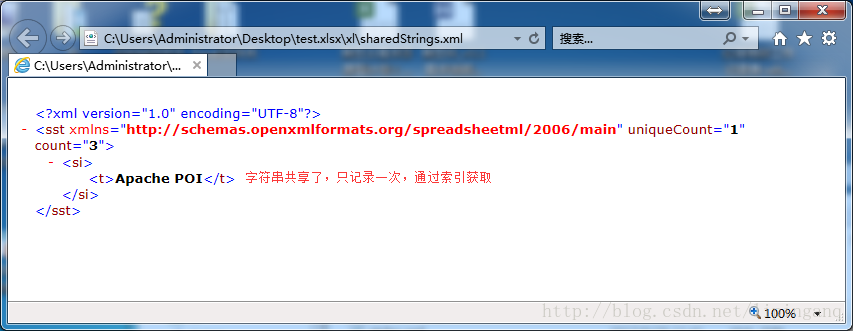
工作簿Workbook大多数字符串具有在单元格级别的格式化样式,即单元格中的整个字符串具有相同的格式应用。 在这些情况下,单元格的格式存储在styles(对于一个styles.xml)中,单元格的字符串可以跨工作表共享 (sharedStrings.xml)。以下代码说明了该示例。
package hssf.sheet.richtextstring;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRichTextString;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
/** * 共享富文本字符串 * */
public class ExportXSSFRichTextSTring_shard {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\test.xlsx");
if (file.exists()) {
file.delete();
}
BufferedOutputStream out = null;
try {
out = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\test.xlsx"));
exportExcel(out);
} finally {
out.close();
}
}
private static void exportExcel(BufferedOutputStream out) throws IOException {
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("共享字符串");
sheet.setColumnWidth(0, 30*256);
sheet.setColumnWidth(1, 30*256);
sheet.setColumnWidth(2, 30*256);
Row row = sheet.createRow(0);
row.setHeightInPoints(20);
row.createCell(0).setCellValue(new XSSFRichTextString("Apache POI"));
row.createCell(1).setCellValue(new XSSFRichTextString("Apache POI"));
row.createCell(2).setCellValue(new XSSFRichTextString("Apache POI"));
workbook.write(out);
}
}
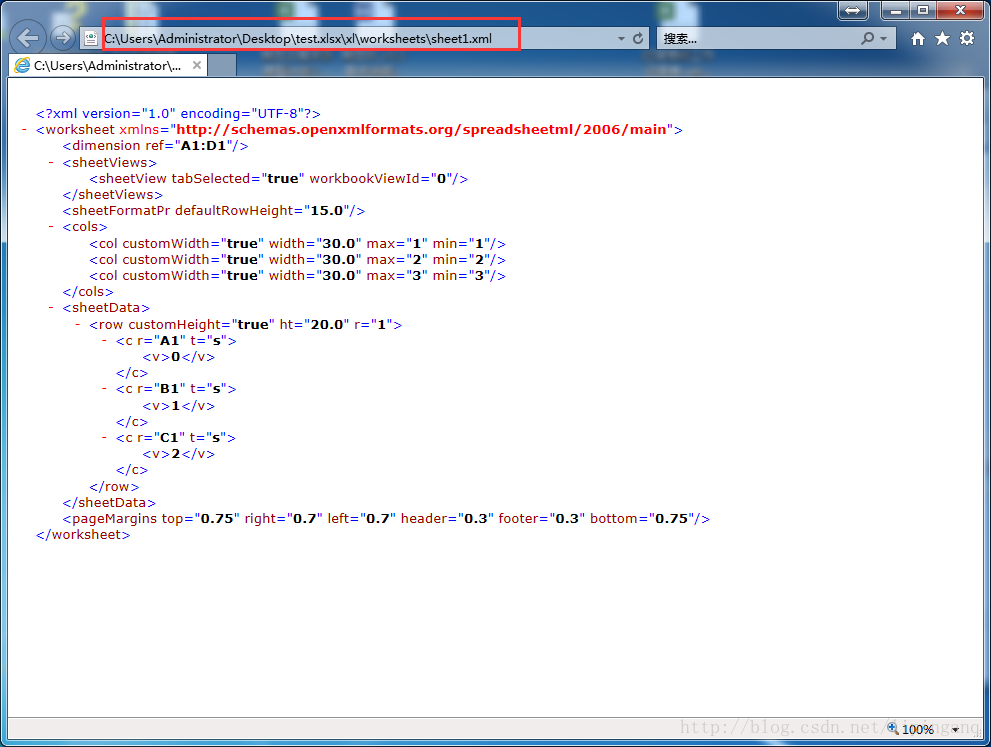
上述3个单元格都使用了工作簿Workbook中缓存的共享字符串 - Apache POI3.2 非共享字符串
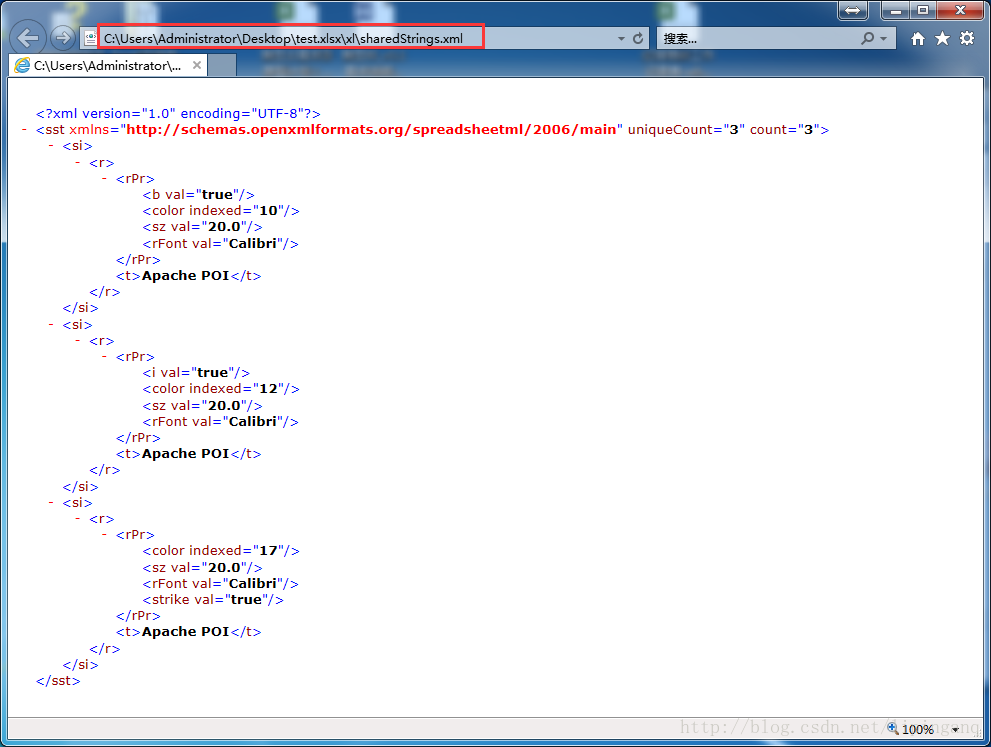
工作簿中的富文本字符串XSSFRichTextString可能具有比单元格级别更细粒度的样式,即可以设置多个样式作用与富文本字符串的不同部分。在这种情况下,样式和文本一起存储在string table中,并被视为工作簿中的唯一条目(entry):
package hssf.sheet.richtextstring;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Font;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.IndexedColors;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.RichTextString;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRichTextString;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class ExportXSSFRichTextString_unique {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\test.xlsx");
if (file.exists()) {
file.delete();
}
BufferedOutputStream out = null;
try {
out = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\test.xlsx"));
exportExcel(out);
} finally {
out.close();
}
}
/** * @param out * @throws IOException */
private static void exportExcel(BufferedOutputStream out) throws IOException {
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("共享字符串");
sheet.setColumnWidth(0, 30*256);
sheet.setColumnWidth(1, 30*256);
sheet.setColumnWidth(2, 30*256);
Row row = sheet.createRow(0);
row.setHeightInPoints(20);
RichTextString s1 = new XSSFRichTextString("Apache POI");
Font font1 = workbook.createFont();
font1.setBold(true);
font1.setColor(IndexedColors.RED.getIndex());
font1.setFontHeightInPoints((short)20);
s1.applyFont(font1);
row.createCell(0).setCellValue(s1);
RichTextString s2 = new XSSFRichTextString("Apache POI");
Font font2 = workbook.createFont();
font2.setItalic(true);
font2.setColor(IndexedColors.BLUE.getIndex());
font2.setFontHeightInPoints((short)20);
s2.applyFont(font2);
row.createCell(1).setCellValue(s2);
RichTextString s3 = new XSSFRichTextString("Apache POI");
Font font3 = workbook.createFont();
font3.setStrikeout(true);
font3.setColor(IndexedColors.GREEN.getIndex());
font3.setFontHeightInPoints((short)20);
s3.applyFont(font3);
row.createCell(2).setCellValue(s3);
workbook.write(out);
}
}版权说明 : 本文为转载文章, 版权归原作者所有 版权申明
原文链接 : https://blog.csdn.net/lipinganq/article/details/78132470
内容来源于网络,如有侵权,请联系作者删除!
上一篇:POI 字体Font